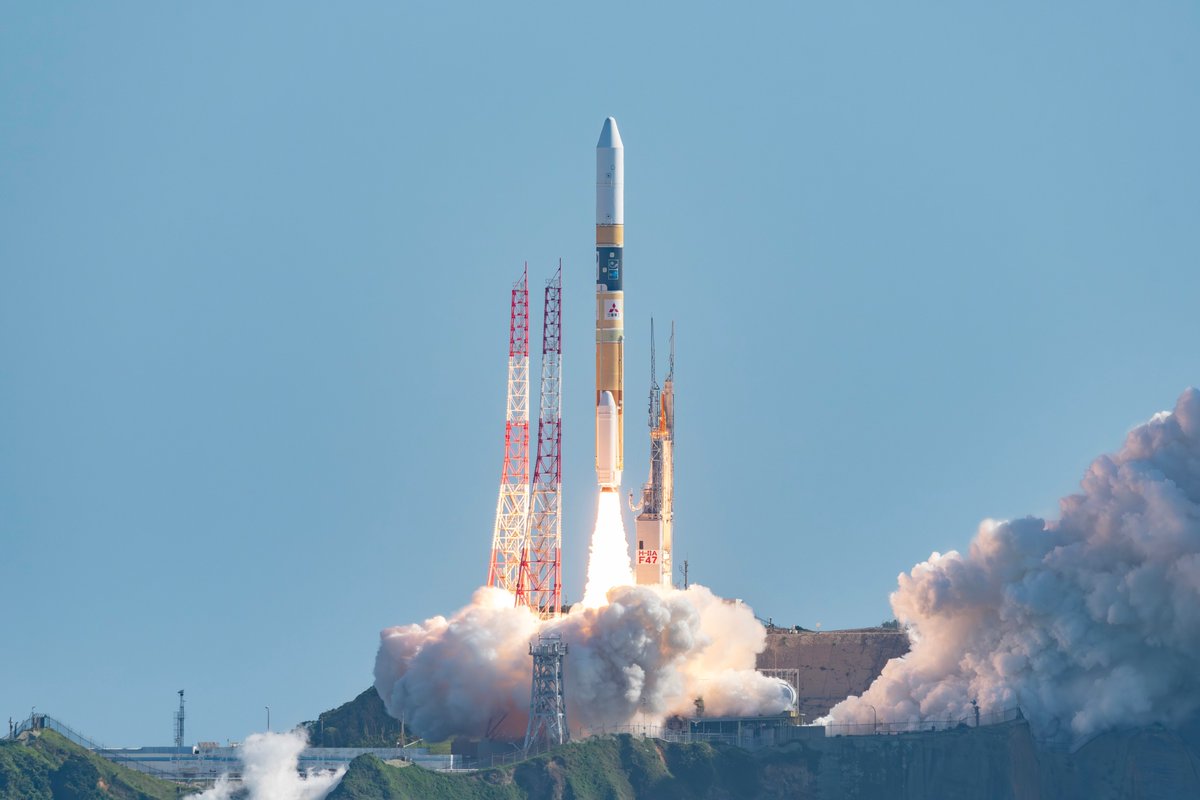

Launch
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
H-IIA 202 | GOSAT-GW (Ibuki GW)
- Mission
- rocket
- Pad
- Agency
Mission
GOSAT-GW (Ibuki GW)
Earth Science
Sun-Synchronous Orbit
GOSAT-GW (Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite Greenhouse gases and Water cycle), also known as Ibuki GW and formerly known as GOSAT 3, is JAXA's next generation satellite to monitor the greenhosue gases like carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. It is the follow on to the GOSAT 2 (Ibuki 2) and GCOM-W (Shizuku) missions. GOSAT-GW will have two missions: greenhouse gases observation for Japan's Ministry of the Environment and the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES), and water-cycle observation for JAXA. By developing the GOSAT-GW satellite, Mitsubishi Electric will contribute to measures for preventing disasters attributed to global warming and climate change, and to advance scientific and technological methods that enable more accurate prediction of climate change. In December 2013, Mitsubishi Electric (MELCO) was selected as the prime contractor for the spacecraft and the instruments.
Status
Launch Successful
The launch vehicle successfully inserted its payload(s) into the target orbit(s).
Pad
Location
Asia/Tokyo
Tanegashima Space Center, Japan
The Tanegashima Space Center is the largest rocket-launch complex in Japan. It is located on the southeastern tip of Tanegashima, an island located south of Kyushu, an island and region and Japan. It was established in 1969 when the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) was formed, and is now run by JAXA. The activities that take place at TNSC include assembly, testing, launching, and tracking satellites, as well as rocket engine firing tests.
97
0
Location Image

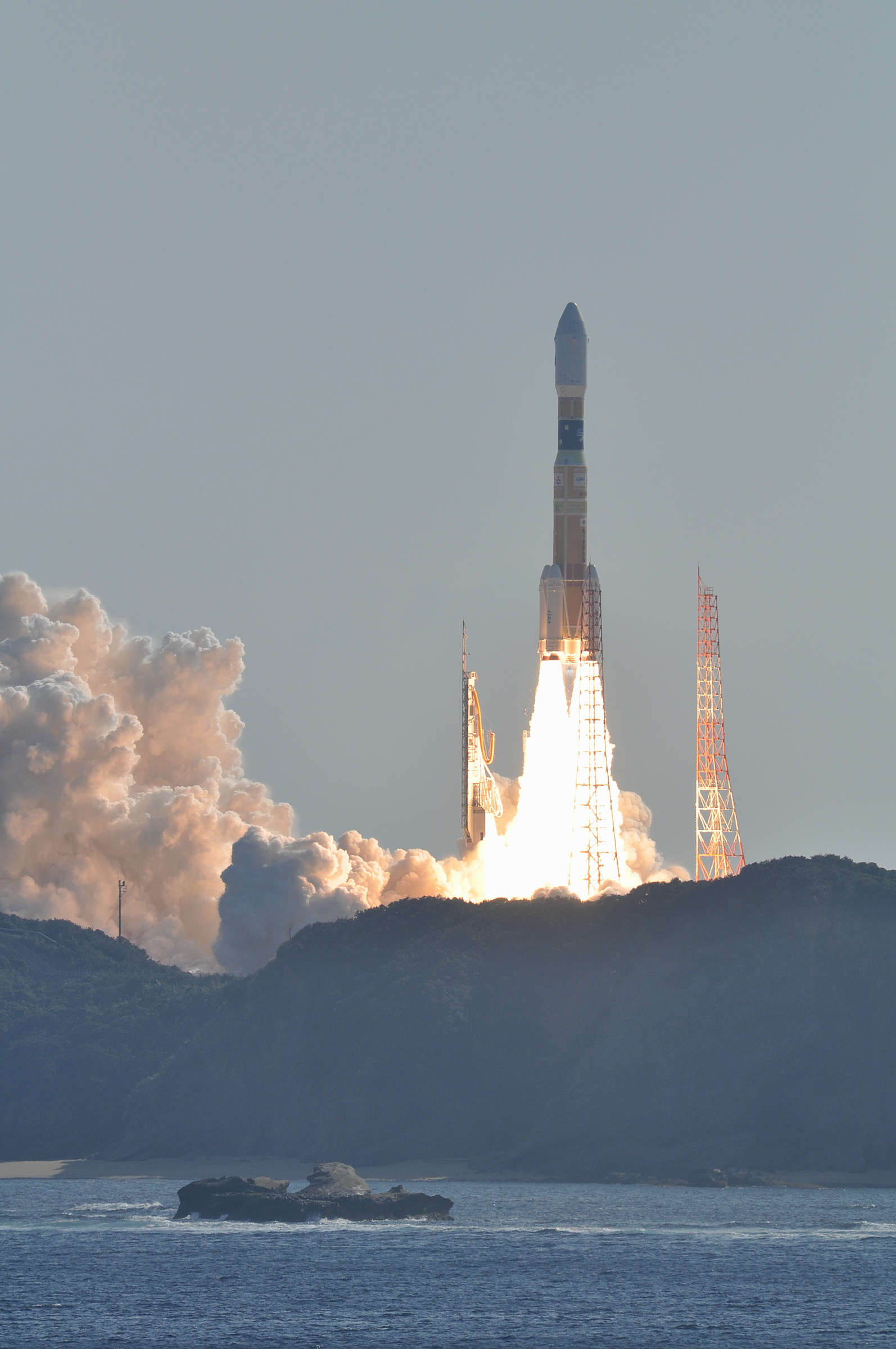
Rocket

H-IIA 202
H-IIA (H2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. The liquid-fueled H-IIA rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit, to launch a lunar orbiting spacecraft, and to launch Akatsuki, which studied the planet Venus. Launches occur at the Tanegashima Space Center.
Family: H-II
Variant: 202
Details
Min stage: 2
Max stage: 2m
Length: 53.0m
Diameter: 4.0
First Flight: Aug. 29, 2001
Total launch count: 35
Successful launches: 35
Consecutive successful launches: 35
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) capacity: 10000kg
Launch cost: US$90000000
Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO) capacity: 4100kg
Manufacturer
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Commercial
JPN
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. is a Japanese multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group. MHI's products include aerospace components, air conditioners, aircraft, automotive components, forklift trucks, hydraulic equipment, machine tools, missiles, power generation equipment, printing machines, ships and space launch vehicles. Through its defense-related activities, it is the world's 23rd-largest defense contractor measured by 2011 defense revenues and the largest based in Japan.
1884
President: Seiji Izumisawa
H-I, H-II, H-III
Kounotori | HTV



Agency

Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
Type: Government
Details